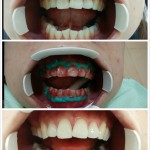
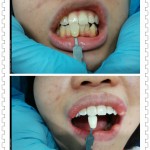
Dental bleaching, also known as tooth whitening, is a common procedure in dentistry, whitening restores natural tooth color and bleaching whitens beyond the natural color.Teeth whitening has become the most requested procedure in cosmetic dentistry today.
Bleaching methods use carbamide peroxide and hydrogen peroxide. The peroxide oxidizing agent penetrates the porosities in the rod-like crystal structure of enamel and breaks down stain deposits in the dentin. Power bleaching uses light to accelerate the process of bleaching in a dental office.
Methods
Dental color shades

The dentist should examine the patient thoroughly: take a health and dental history (including allergies and sensitivities), observe hard and soft tissues, placement and conditions of restorations, and sometimes x-rays to determine the nature and depth of possible irregularities.
The whitening shade guides are used to measure tooth color. These shades determine the effectiveness of the whitening procedure, which may vary from two to seven shades. The effects of bleaching can last for several months, but may vary depending on the lifestyle of the patient.
White-spot decalcification may be highlighted and become more noticeable directly following a whiting process, but with further applications the other parts of the teeth usually become more white and the spots less noticeable.
Bleaching is not recommended if teeth have decay or infected gums. It is least effective when the original tooth color is grayish and is most effective with yellow discolored teeth. However, whitener does not work where bonding has been used and neither is it effective on tooth-color filling. Other options to deal with such cases are the porcelain veneers or dental b
Bonding, which also masks tooth stains, is when a thin coating of composite material is applied to the front of a person’s teeth and then cured with a blue light. A veneer can also mask tooth discoloration.